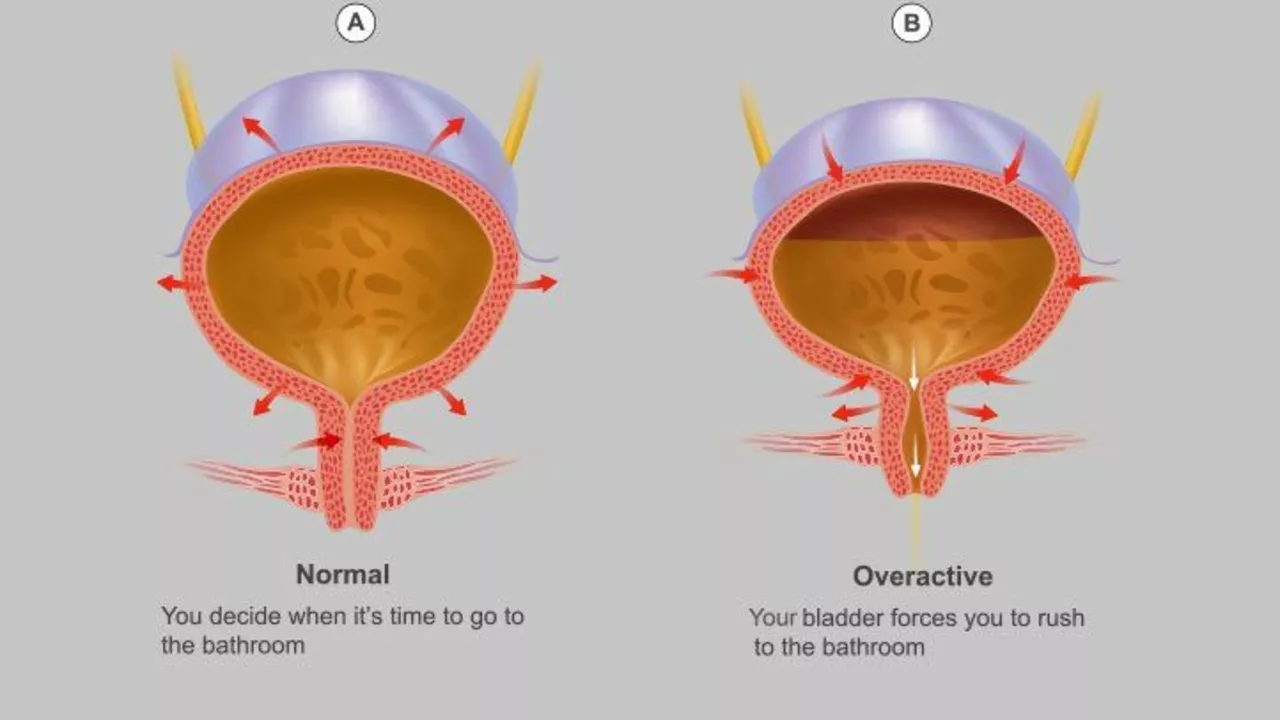
Understanding Overactive Bladder
Before we delve into the future of overactive bladder treatment, it's essential to understand what an overactive bladder is. It's a condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing frequent urination, urinary urgency, and, in some cases, incontinence. It's not just a physical issue, but it can also significantly impact a person's emotional and social life. Many current treatments focus on managing symptoms rather than addressing the underlying cause.
The Limitations of Tolterodine
Tolterodine has been a go-to drug for overactive bladder for years. It works by relaxing the bladder muscles and reducing bladder contractions. However, like all medications, tolterodine comes with its set of limitations. Some patients experience side effects such as dry mouth, constipation, and blurred vision. Additionally, the drug may not be effective for everyone and can have potential interactions with other medications.
Emerging Drug Therapies
Thankfully, the future of overactive bladder treatment looks promising, with several emerging drug therapies on the horizon. These include newer drugs that work differently than tolterodine, targeting different aspects of bladder function and potentially offering fewer side effects. For instance, some drugs under investigation focus on increasing bladder capacity or reducing the urgency to urinate.
Botulinum Toxin Injections
Botulinum toxin, commonly known as Botox, has shown promise in treating overactive bladder when other treatments have failed. It works by relaxing the bladder muscles, reducing the urge to urinate and increasing bladder capacity. However, it's worth noting that while Botox can provide relief, it's not a cure and the injections need to be repeated every few months.
Neuromodulation Therapies
Another breakthrough in the treatment of overactive bladder is neuromodulation therapies. These treatments work by sending mild electrical pulses to the nerves that control bladder function. The two main types of neuromodulation therapies are sacral nerve stimulation (SNS) and percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS). Both have shown success in managing symptoms of overactive bladder.
Personalized Medicine
In the future, we may see more personalized approaches to treating overactive bladder. This could involve genetic testing to identify which patients are most likely to respond to specific treatments. It could also involve tailoring treatments to a patient's specific symptoms, lifestyle, and preferences. Personalized medicine has the potential to improve treatment effectiveness and patient satisfaction.
Lifestyle Interventions
While advancements in drug therapies and procedures are exciting, it's also important not to overlook the role of lifestyle interventions in managing overactive bladder. Simple changes such as reducing fluid intake, avoiding bladder irritants, and practicing bladder training can make a significant difference in managing symptoms. Future treatment plans may incorporate more comprehensive lifestyle interventions alongside medication and procedures.
Conclusion: Hope for the Future
While we've come a long way in treating overactive bladder, there's still much more to learn. The future holds promise for more effective treatments, with fewer side effects and more personalized approaches. Despite the challenges, there's reason for optimism. With continued research and development, we can look forward to a future where overactive bladder is no longer a major disruption in people's lives.


Reginald Maarten
Tolterodine isn't the problem-it's the lazy prescribing culture. Doctors treat symptoms like they're fixing a leaky faucet without checking the pipes. The real issue? No one's studying bladder neuroplasticity long-term. We're just swapping one anticholinergic for another.
Jonathan Debo
The term 'overactive bladder' is, frankly, a misnomer-it implies the bladder is malfunctioning, when in reality, it's the central nervous system's dysregulation of the micturition reflex that's at fault. The literature is replete with studies-see, for instance, de Groat et al., 2015-that demonstrate cortical hyperexcitability as the root cause. Yet, we persist in pharmacologically silencing the bladder, not the brain.
Robin Annison
It's interesting how we keep looking for the next magic pill, but rarely ask why the bladder becomes overactive in the first place. Maybe it's not about fixing the organ, but about restoring balance to the whole system-stress, sleep, pelvic floor tone, even emotional repression. We treat the symptom, not the silence behind it.
Abigail Jubb
Botox injections? That's what they're calling it now? It's not medicine-it's a temporary bandage on a systemic collapse. And don't get me started on how insurance refuses to cover it unless you've already suffered three years of humiliation and urinary accidents. This isn't healthcare. It's a performance art for corporate profits.
George Clark-Roden
I’ve been living with this for 12 years. I’ve tried everything. Tolterodine made me feel like a zombie. Botox gave me temporary relief but left me terrified of UTIs. PTNS? I cried after the first session-it was the first time in years I slept through the night. No drug, no procedure, no ‘breakthrough’ has ever given me back my dignity like that. Don’t dismiss the quiet victories.
Hope NewYork
lol so btox is the future? yeah right. they just wanna keep us hooked on treatments that cost 5k per shot. meanwhile, the real cause? glyphosate in your water. it messes with your nerves. google it. no one wants to talk about it because big pharma owns the FDA. wake up.
Bonnie Sanders Bartlett
I’ve seen so many people struggle with this. It’s not just about medicine. It’s about being heard. A simple conversation with a therapist who understands pelvic floor tension, or a gentle yoga class designed for bladder health-those things change lives. Don’t underestimate the power of kindness in healing.
Melissa Delong
The entire premise of this article is dangerously misleading. Neuromodulation? Botox? These are not treatments-they are corporate experiments disguised as medical innovation. The FDA approval process is a revolving door. The real solution? Stop drinking tap water. It contains fluoride, chlorine, and traces of antidepressants. Your bladder is reacting to toxins, not neurological dysfunction.
Marshall Washick
I remember the first time I didn’t have to plan my entire day around a bathroom. It wasn’t because of a drug. It was because I started doing pelvic floor exercises for ten minutes a day. No one talks about that. No one sells that. But it worked. Maybe the future isn’t in new drugs-it’s in rediscovering what we already knew.
Abha Nakra
In India, we’ve used herbal blends like Punarnava and Gokshura for centuries. Modern science is just catching up. Why aren’t we studying these alongside pharmaceuticals? It’s not about replacing one thing with another-it’s about integrating. Bladder health is holistic. Why treat it like a machine?
Neal Burton
They want you to believe Botox is progress. But the truth? It’s the same old pattern-profit-driven, symptom-focused, emotionally detached. They don’t care if you’re dry-mouthed and constipated. They care about the quarterly earnings report. This isn’t medicine. It’s capitalism with a stethoscope.
Tamara Kayali Browne
The cited studies on mirabegron are methodologically flawed. Sample sizes are inadequate, control groups are poorly matched, and long-term safety data is nonexistent. Furthermore, the term 'personalized medicine' is being weaponized as a marketing buzzword. There is no validated genetic biomarker for OAB treatment response. This article is dangerously optimistic.
Nishigandha Kanurkar
They’re hiding the truth. The real cause of overactive bladder is 5G radiation. It disrupts the sacral nerve signals. That’s why it’s worse in cities. That’s why it’s rising. They don’t want you to know because the telecom companies own the pharmaceutical industry. You think Botox fixes it? No. It just masks the signal interference. Turn off your Wi-Fi. Use airplane mode. It’s the only real solution.
Lori Johnson
I love how everyone’s obsessed with the new drugs but ignores the simplest thing: timing your fluids. I used to drink 3 liters of water a day because I thought it was ‘healthy.’ Turns out, that’s like pouring gasoline on a fire. Cut back after 6 PM. Avoid caffeine. You’d be shocked how much that helps. No pill needed.
Tatiana Mathis
I’ve worked with dozens of patients over the years who felt invisible because their symptoms were dismissed as ‘just aging’ or ‘not serious.’ The real breakthrough isn’t a new drug-it’s the shift in how we listen. When a clinician sits down, makes eye contact, and says, ‘Tell me what this has cost you,’ that’s when healing begins. The science matters, but so does the humanity behind it.
Michelle Lyons
They’re all lying. The FDA knows that mirabegron causes long-term nerve damage. They’re covering it up because they’re paid by the drug companies. I saw the leaked memo. It was buried under a ‘Phase III’ report. If you look at the real data-under the ‘supplemental appendix’-you’ll see the spike in peripheral neuropathy cases. Don’t trust anything you read.
Cornelle Camberos
The entire paradigm of overactive bladder management is predicated upon a flawed biomedical model that reduces a complex neurophysiological phenomenon to a single organ malfunction. Such reductionism is not only scientifically untenable but ethically indefensible. Until the medical establishment embraces a systems-biology approach-integrating autonomic, psychological, and environmental determinants-we shall remain mired in palliative mediocrity.